

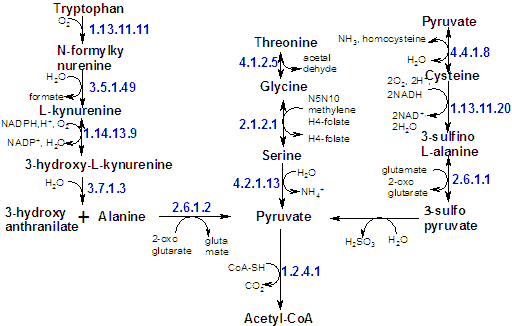
| Alanine, Cysteine, Glycine, Serine, Tryptophan and Threonine are degraded to pyruvate |
|
| |
Pyruvate is the entry point of the three-carbon amino acids - alanine, serine, and cysteine - into the metabolic mainstream. |
The transamination of alanine directly yields pyruvate (the same reaction of the cori cycle). |
Serine is deaminated to pyruvate by serine dehydratase. |
Cysteine can be converted into pyruvate by several pathways, with its sulfur atom emerging in H2S, SO32-, or SCN-. |
| The carbon atoms of three other amino acids can be converted into pyruvate: |
|
-Glycine can be converted into serine by enzymatic addition of a hydroxymethyl group, or it can be cleaved to give CO2, NH4+, and an activated one-carbon unit. |
|
-Threonine can give rise to pyruvate by way of aminoacetone. |
|
Three carbon atoms of tryptophan can emerge in alanine, wich can be converted into pyruvate. |