

| Methionine, Threonine, Valine and Isoleucine catabolism |
 |
| |
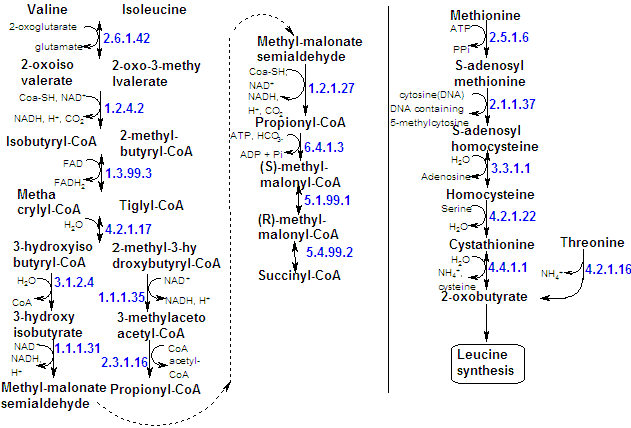
| The catabolism pathways of Methionine, Isoleucine and Valine are very extensive, but there are some common points that make them more simple. The first four steps in degradation of isoleucine and valine are catalyzed by the same enzymes. propionyl-CoA and then methylmalonyl-CoA are intermediates in the breakdown of these three nonpolar amino acids. Methylmalonyl-CoA is converted to succinyl-CoA in one single step by an intramolecular rearrangement. |
| Since thre's a great number of carbon-carbon satturated linkages in these molecules, the pathways are very similar to fatty acids catabolism. |
| The a-keto acids of the three amino acids are decarboxylated . |
The degradation pathway of valine and isoleucine resemble that of leucine. All three amino acids are iniatially transaminated to the corresponding a-keto acid (by the same enzyme complex), wich is then oxidatively decarboxylated by the branched-chain a-keto dehydrogenase to yield a CoA derivative. The subsequent reactions are like those of fatty acid oxidation. Isoleucine yields acetyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA, whereas valine yields CO2 and propionyl-CoA. |
| Threonine can also be degraded by another pathway. It can also give rise to pyruvate by way of aminoacetate. |