

|
Amino acids Biosynthesis |
 |
| |
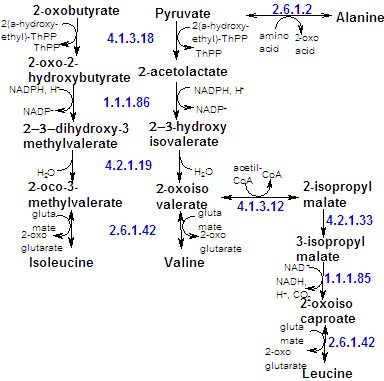
Valine, isoleucine and leucine, all essential amino acids, are the pyruvate family. Pyruvate is the source of 2 of the 6 carbon atoms of Isoleucine, and aspartate is the precursor of the other 4. Thereby, Isoleucine is also an aspartate family member. |
Valine and isoleucine are both synthesized by the same five-step pathway, the only difference being in the first step of the series. |
| The leucine biosynthetic pathway branches off from the valine pathway at a-ketoisovalerate. The reactions from a-ketoisovalerate to a-ketoisocaproate are reminiscent of the first three reactions of the citric acid cycle. Here, acetyl-CoA condenses with a-ketoisovalerate, wich then undergoes a dehydration/hydration reaction, followed by oxidative decarboxylation and transamination, to yield leucine. |
Pyruvate is the a-keto acid of alanine, so it's also precursor of alanine, yielding it by amidation(transamination), as in the cori cycle. |