Acetate
 |
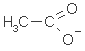 |
 |
| |
Name
Acetate
Acetic acid
Ethanoic acid
Acetic acid
Ethanoic acid
Formula
C2H4O2
Classification
It's a two carbons fatty acid.
Pathways
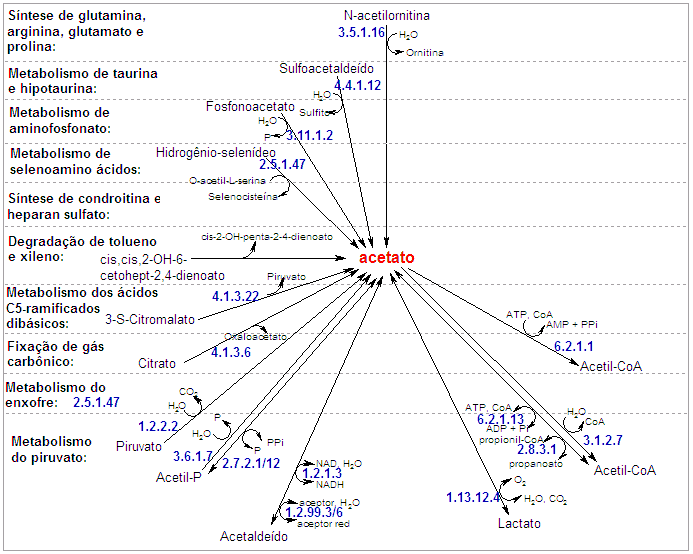
Synthesis of glutamine, arginine, glutamate and proline (3D)
Fermentation (3D)
Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism (Kyoto University)
Aminophosphonate metabolism (Kyoto University)
Selenoamino acid metabolism (Kyoto University)
Chondroitin / Heparan sulfate biosynthesis (Kyoto University)
Toluene and xylene degradation (Kyoto University)
C5-Branched dibasic acid metabolism (Kyoto University)
Reductive carboxylate cycle (CO2 fixation) (Kyoto University)
Sulfur metabolism (Kyoto University)
Fermentation (3D)
Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism (Kyoto University)
Aminophosphonate metabolism (Kyoto University)
Selenoamino acid metabolism (Kyoto University)
Chondroitin / Heparan sulfate biosynthesis (Kyoto University)
Toluene and xylene degradation (Kyoto University)
C5-Branched dibasic acid metabolism (Kyoto University)
Reductive carboxylate cycle (CO2 fixation) (Kyoto University)
Sulfur metabolism (Kyoto University)
Other comments
In the vegetals, some invetebrates and microorganisms, the acetate can serve both as an energy-rich fuel, and as a phosphoenolpyruvate source to the synthesis of carbohydrates (glyoxalate cycle). (1)