|
Phospholipids synthesis |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
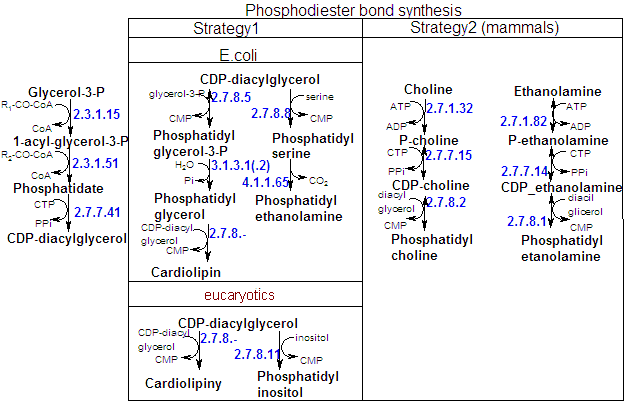
| Phospholipidis synthesis in Escherichia coli |
| The three most important phospholipids in E. coli are: phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol; and cardiolipin. All of them are synthesized from CDP-diacylglycerol. |
| The enzymes are in the inner membrane of teh bacteria. |
| Phospholipidis synthesis in eucaryotics cells |
| These substances are synthesized in membranes, mostly on the cytosolic face of the endoplasmatic reticulum, and from there are transported to their final cellular destination. |
Glycerophospholipids |
Phosphoglycerolipids can be synthesized in several ways. |
The triacylglycerol precursors 1,2-diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid are also the precursor of certain glycerophospholipids. Activated phosphate esters of the polar head groups react with the C3-OH group of 1,2-diacylglycerol to form the phospholipid's phosphodiester bond. In some cases the phosphoryl group of phosphatidic acid is activated and reacts with the unactivated polar head group. |
Sphingophospholipids |
Only one major phospholipid contains ceramide (N-acetyl-sphingosine) as its hydrofobic tail: sphingomyelin. The main route of sphingomyelin synthesis occurs through donation of the phosphocoline group pf phosphatidylcholine to N-acetylsphingosine. |
| |

