

Deoxyribonucleotides synthesis |
 |
|
|
"de novo" synthesis |
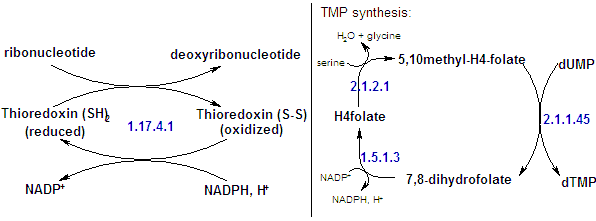
| In mammals, as is other organisms, deoxyribonucleotides are synthesized from their corresponding ribonculeotides by the reduction of ther C2' position. Enzymes that catalyze these reaction are named ribonucleotide reductases, and their substrates are diphosphate ribonucleotides. The physiological reducing agent is a small molecular weight protein, the thioredoxin. |
Thymidylate synthase |
|
Since DNA constains thymine instead of uracile, the dTMP is synthesized by methylation of dUMP. The dUMP is generated by the deamination of dCMP, by deoxycytidilate deaminase: |
|
dCMP + H2O |
|
dUMP can also be generated through the hydrolysis of dUTP by dUTP diphospho-hydrolase: |
|
dUTP + H20
|
Salvage synthesis |
|
Thymine, as uracil, is converted to dTMP following the reaction belllow: |
| Thymine + deoxyribose-1-P |
Thymidine + ATP |
|
Thymidine phosphorilase was purified from mammals and bacterias. Thymidine is its main substrate, but deoxyuridine and its C5' substituted derivatives are also cleaved by this enzyme. Thyimidine Kinase is widely distributed. |