

|
Purines are degraded to uric acid and other products |
 |
| |
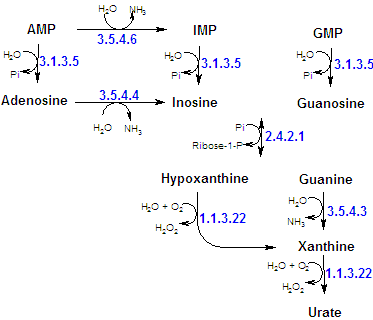
| After the hydrolytically degradation of purine nucleotides to the correspondent nucleosides, inosine and guanosine are cleaved to free bases and ribose-1-P (or deoxyribose-1-P) by purine nucleosides phosphorylase. Adenosine and deoxyadenosine are not substrates of the phosphorylase, but an aminohydrolysis (deaminase) very active in muscles and other tissues convert most of the AMP to IMP. |
| The inosine is then phosphorylated to hypoxanthine. Most of them enter in the salvage pathqyas, and only 10% are degraded by oxidation - xanthine oxidase (high concentration in the liver and intestinal mucosa, and small concentrations in other tissues) oxydizes hypoxanthine to xanthine and then to uric acid. Xanthine can also be produced from guanine by guanine deaminase. |
|
All mammals but the primates can oxidize urate by an hepatic enzyme, urate oxidase. The product allantoin is excreted. In primates ans birds, that lack this enzyme, urate is the final step in the catabolism of purines. |