

Cholesterol
synthesis |
 |
| |
| Cholesterol is an steroid that modulates the fluidity of eukaryotic membranes. Cholesterol is also the precursor of steroid hormones. |
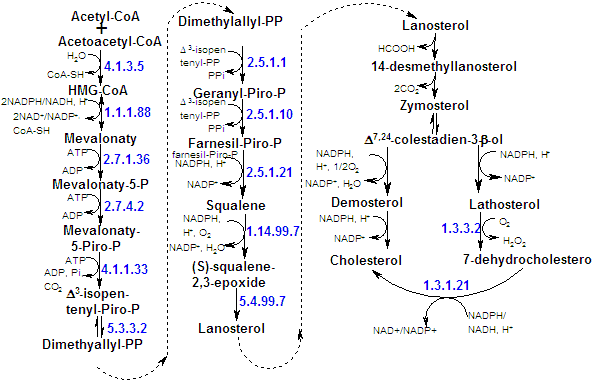
All of the carbon atoms of cholesterol are derived from acetate, that is first converted to isoprene units (C5) - units that have the carbon skeleton of isoprene. Acetyl-CoA is converted to isoprene units by a series of reactions that begins with formation of HMG-CoA (hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA). HMG-CoA is the precursor of two isoprenoid intermediates, isopentenyl pyrophophate and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. |
Isoprene units are condensed to form a linear precursor to cholesterol and then cyclized. |
Four isopentenyl-PP and two dimethylallyl-PP condense to form the C30 cholesterol precursor squalene (open-chain hydrocarbon). |
Then squalene is cyclized to form the tetracyclic steroid skeleton. |