Amino
acids Biosynthesis Phenylalanine and Tyrosine |
 |
| |
|
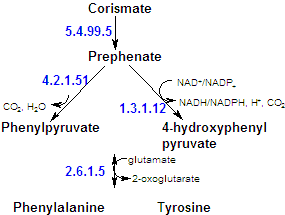
Phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan, the aromatic amino acids, are syntehsized by a commom pathway. The precursors are the glycolytic intermediate phosphoenolpyruvate and erythrose-4-P (an intermediate of the pentose-P pathway). Their condensation forms a C7 compound that cyclized and is ultimately converted to chorismate, the branch point for tryptophan biosynthesis. Chorismate is either converted to antharanilate and then on to tryptophan, or to prephenate and on to either tyrosine or phenylalanine. Altough mammals synthesize tyrosine by the hydroxylation of phenylalanine, many microorganisms synthesize it directly from prephenate. |
The synthesis of aromatic amino acids only occurs in plants and microorganisms. |
| |

