Serine, Glycine and Cysteine
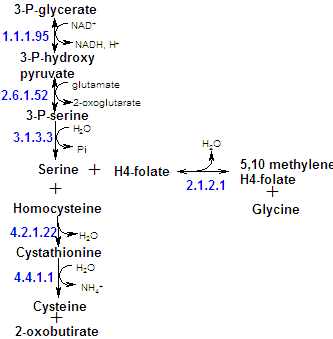
Serine is formed from the glycolytic intermediate 3-phosphoglycerate in a three reaction pathway.
Serine participates in glycine synthesis in two ways: Direct conversion of serine to glycine in a reaction that also yields N5-N10-methylene-THF; and condensation of the with CO2 and NH4+ by glycine synthase.
Cysteine is synthesized in animals from serine and homocysteine, a breakdown product of methionine. The conversion of serine into cysteine requires the substitution of a sulfur atom derived from methionine for the side-chain oxygen atom. Since cysteine's sulfhydryl group is derived from the essential amino acid methionine, cysteine is really an essential amino acid.

