

Lipids Catabolism
Fatty acids activation
 |
|
|
|
Activation |
|
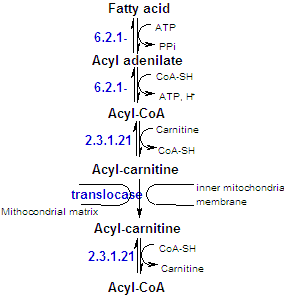
Before fatty acdis can be oxidized, they must be "primed" for reaction in an ATP-dependent acylation reaction to form fatty acyl-CoA. This proccess is catalyzed by a family of acyl-CoA synthetases. |
Transport across the Mitochondrial Membrane |
|
|
Although fatty acids are activated for oxidation in the cytosol, they are oxidized in the mitochondria. A long-chain fatty acyl-CoA cannot directly cross the inner mitochondrial membrane. Rather, its acyl portion is first trasnferred to carnitine by carnitine palmitoyl transferase I. The translocation proccess itself is mediated by a specific carrier protein that transports acyl-carnitine into the mitochondrion while tranporting free carnitine in the opposite direction. Carnitine palmitoyl transferase II, loacated in the internal surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane transfer the acyl group to a Coa molecules from the mitochondrial pool, releasing the carnitine. |
|
The cells thereby maintains separate cytosolic and itochondrial pools of CoA. |
|
|
|
|