

Ketone bodies metabolism
 |
|
| |
|
| The acetyl-CoA formed in fatty acid oxidation enters the citric acid cycle only if fat and carbohydrate degradation are appropriated balanced. The reason is that the entry of acetyl-CoA into the citric acid cycle depends on the availability of oxaloacetate for the formation of citrate. |
|
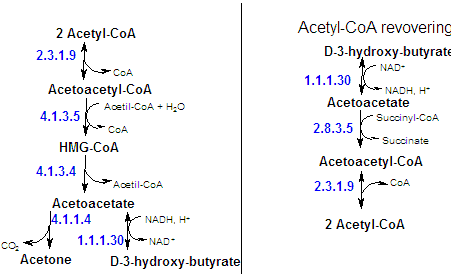
In fasting or diabetes, oxaloacetate is consumed to form glucose ny the gluconeogenic pathway and hence is unavailable for condensation with acetyl-CoA. Under these conditions, acetyl-coA is diverted to the formation of acetoacetate and D-3-hydroxybutyrate. This procces is known as ketogenesis, wich occurs primarly in liver mitochondria. Acetoacetate, D-3-hydroxybutyrate and acetone are sometimes referred to as ketone bodies. |
|
The brain, under normal circumstances, uses only glucose as its energy source, but during starvation ketone bodies become the brain's major fuel source. |
|