 |
 |
 |
Click on the image to start downloading the PDB file (tridimensional and interactive).
5.Acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds, other than peptide bonds
1.In linear amides
H2O
NH3
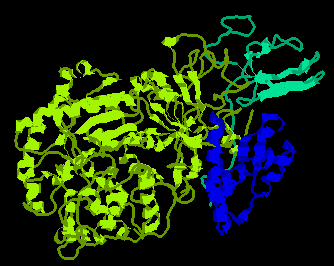
Urease is a nickel-binding enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea to carbon dioxide and ammonia. Historically, it was the first enzyme to be crystallized (in 1926). It is mainly found in plant seeds, microorganisms and invertebrates. In plants, urease is a hexamer of identical chains. In bacteria, it consists of either two or three different subunits (a, b and g).
Urease binds two nickel ions per subunit; four histidine, an aspartate and a carbamated-lysine serve as ligands to these metals; an additional histidine is involved in the catalytic mechanism.
As signatures for this enzyme, it has been selected a region that contains two
histidine that bind one of the nickel ions and the region of the active site
histidine.
Reference